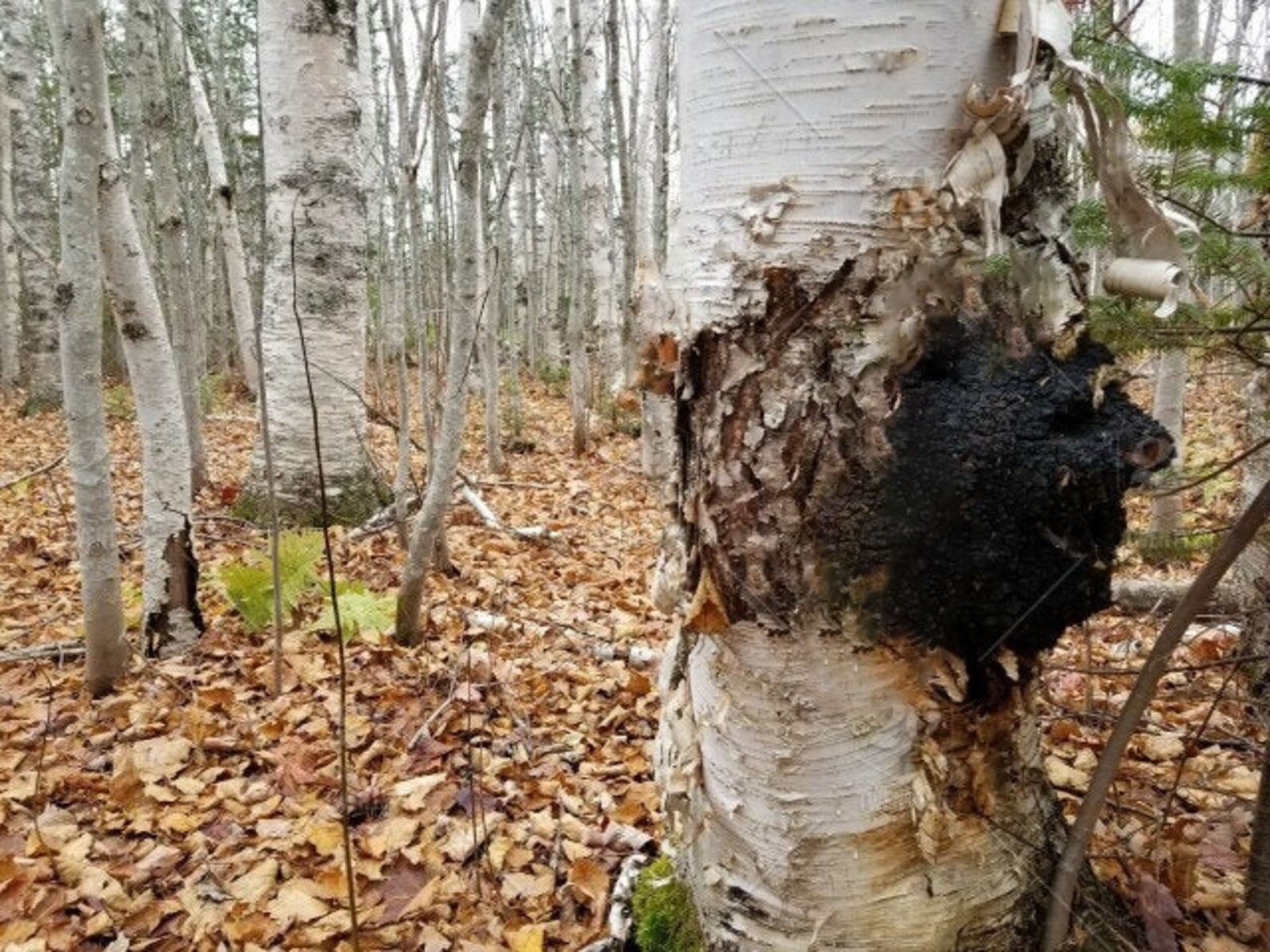

Chaga Water: Exploring Its Potential for Pregnant and Postpartum Health
-
Preparation:
-
Start with dried Chaga chunks or powder. If you're using chunks, you'll need to break them down into smaller pieces.
-
-
Infusion:
-
Place the Chaga in cold or room-temperature water. The ratio is typically about 1-2 tablespoons of Chaga per liter of water, but this can be adjusted for taste or potency.
-
Let it sit for 4 to 8 hours or overnight in the fridge. This cold extraction method is believed to leach out beneficial compounds without the bitterness that hot water can extract.
-
-
Strain:
-
Strain the liquid to remove the Chaga pieces. The water will have a dark, tea-like color.
-
-
Boiling Water:
-
Use 1-2 teaspoons of Chaga powder or small pieces for one cup of water. If using chunks, they can be reused several times before losing potency.
-
-
Steeping:
-
Bring water to a boil, then reduce to a simmer. Add the Chaga to the hot water and simmer for 15 to 20 minutes. The longer you steep, the stronger the tea will be.
-
-
Strain and Serve:
-
Strain the tea to remove the Chaga bits. You can drink it as is or add honey, lemon, or other flavors for taste. Chaga tea has an earthy flavor, which some find bitter without additives.
-
-
Antioxidant Properties: Chaga's high antioxidant content could potentially help combat oxidative stress, which is particularly important during pregnancy when the body is under additional strain.
-
Immune Support: Chaga is known for its immune-boosting capabilities, which might help in reducing the risk of infections, although this should be monitored carefully during pregnancy.
-
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Inflammation can be an issue during pregnancy, and Chaga's anti-inflammatory properties might offer relief, though this needs to be balanced with the potential hormonal effects.
-
Limited Research: There's insufficient research on the safety of Chaga during pregnancy. Its effects on hormones like estrogen could potentially impact pregnancy, so caution is advised.
-
Safety Concerns: The lack of comprehensive studies means that most sources recommend avoiding Chaga during pregnancy unless under the strict guidance of a healthcare provider.
-
Recovery: Postpartum, Chaga might aid in recovery by supporting the immune system, which can be compromised due to the physical demands of childbirth and breastfeeding.
-
Energy Levels: Its adaptogenic qualities might help with energy regulation, useful for new mothers dealing with sleep deprivation.
-
Antioxidant Support: Continuing antioxidant intake can help counteract the oxidative stress from childbirth and breastfeeding.
-
Lactation: There's no conclusive evidence that Chaga supports or hinders lactation. Some caution against its use due to potential hormonal effects which might affect milk production.
-
Consultation Required: Just like during pregnancy, postpartum women should consult healthcare providers before consuming Chaga. The safety, especially regarding its passage into breast milk, is not well-documented.
-
Quality and Source: Ensure you're using Chaga from a reputable source since it can absorb pollutants from the environment.
-
Dosage: There's no established dosage, so start with small amounts to test for tolerance.
-
Medical Advice: Always discuss with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Disclaimer: Jessie is not a medical expert; always consult with healthcare professionals for advice specific to your situation. Remember, the information here is for educational purposes and does not replace professional medical advice. Do not share your personally identifiable information.


Dejar un comentario
Este sitio está protegido por hCaptcha y se aplican la Política de privacidad de hCaptcha y los Términos del servicio.